Why sleep is essential for health:
One must get enough sleep in order to maintain the best possible health and well-being. Much like exercise and a healthy diet, sleep may help prevent a number of health issues, including heart disease and depression.
Contemporary life in the United States and many other countries does not always value getting enough sleep. But it's important that people consistently try to get enough sleep.
According to health experts, the advantages of getting a good night's sleep include the following:
Better memory and performance:
The short- and long-term effects of interrupted sleep on health were examined in a 2017 study Trusted Source. Researchers found that sleep is related to a number of different brain processes, including:
Memory:

Image Source: Times of India
Sleep disruption may impact the processing and creation of memories. Sleep disruption has an impact on how well people perform at work, in school, and in other situations. This includes attention, emotional reactivity, judgment, and decision-making.
Cognitive function may be impacted by disturbed sleep because stress hormones are affected.
Children's sleeping habits may have a direct impact on their behavior and academic performance, according to a 2015 study published in the Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry.
Lower weight gain risk:

Image Source: clinicaladvisor.com
The connection between obesity, weight gain, and insufficient sleep is uncertain. Over the years, numerous studies have discovered a link between obesity and erratic sleeping habits. Those who regularly get less sleep than seven hours each night are more likely to have a higher body mass index (BMI) and develop obesity than those who get more sleep, according to a 2018 study. Research has connected sleep deprivation to the hunger hormone ghrelin, salt retention, and inflammatory markers. More research is needed to fully understand the links between inadequate sleep and weight gain. to locate additional sources of knowledge and data regarding the science of sound sleep, which is backed by statistics.
Better calorie regulation:

Image source: NBC NEWS
There is proof that insufficient sleep can cause the body to burn fewer calories in addition to weight gain. For instance, a clinical experiment conducted in 2022 revealed that obese adults who increased their sleep duration consumed fewer calories than a control group. The adults consumed about 270 fewer calories and slept an additional 1 12 hours on average than the control group. Researchers contend that getting more sleep and keeping up a healthy sleep schedule can aid in weight loss and guard against obesity.
Greater athletic performance:

Image Source: post.medicalnewstoday.com
Adults require 7 to 9 hours of sleep each night, but recent research indicates that athletes may require more. Sportspeople and athletes should get enough sleep because it helps the body heal. among other advantages are:
Increased patience.
More energy.
Greater accuracy and quicker reaction times.
Hurt time.
Better mental capacity.
Lower risk of heart disease:
Image Source: Google.com
Hypertension is a heart disease risk factor. A restful night's sleep can also lower the risk of sleeping disorders like pane and improve general heart health.
More emotional and social intelligence:
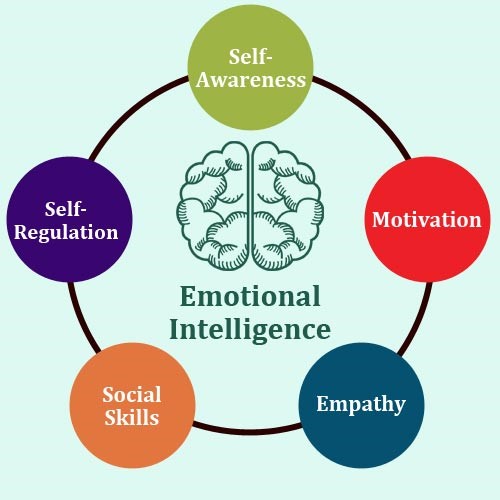
Image source: i.ytimg.com
Emotional and social intelligence and sleep are related. A person who is sleep-deprived is more likely to find it difficult to interpret the emotions and expressions on the faces of others.
477 participants completed questionnaires that examined their sleep habits and emotional intelligence.
Lower inflammation:

Image Source: health.clevelandclinic.org
Getting enough sleep is linked to a decrease in inflammatory reactions in the body. For instance, a 2019 study found a strong correlation, especially in women, between increased sleep irregularity and higher levels of inflammation. A person's body's capacity to control inflammation while they are sleeping may be hampered by irregular sleep patterns, which involve waking up or going to bed at irregular intervals during the night.
Stronger immune system:

Image Source: blog.cirm.ca.gov
The body recovers, repairs, and regenerates itself while you sleep. Immune systems are not an exception. The precise mechanism by which sleep influences the immune system of humans needs further investigation, though.
Stages of sleep:
When a person is sleeping, their body goes through four stages of sleep. Each of these stages encourages a deeper level of sleep, and together they make up non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. Dreams are most frequent during the final stage of sleep, known as rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Each stage is repeated four to six times by the body.
NREM (Light sleep):
![Sleep Stages [4 Types of Sleep Stages] | SleepScore](https://www.sleepscore.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/sleepscore-blog-3_graphic-1-1017x1024.jpg)
Image source: amerisleep.com
During this lightest stage of NREM sleep, a person transitions from being awake to being asleep.
This stage of the process is characterized by a slowing of the heartbeat, breathing, and eye movements.
A person typically spends only 5% of their total sleep time in stage 1, which lasts for a few minutes.
During this time, a person's heart rate slows and their muscles continue to relax. Sleep spindles, which are brief electrical activity spikes, happen as a person's brain waves slow down. Studies show that sleep spindles help with memory consolidation.
In stage 2, sleepers spend about 45% of their total waking hours. This stage typically lasts longer with each cycle, with the first cycle taking around 25 minutes.






